Intestinal Permeability And Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Intestinal permeability and inflammatory bowel disease. And disruption of the cell cycle. Recent evidence suggests that some food components can influence the integrity of the intestinal barrier and thus its permeability. Pathogenesis Clinical Evaluation and Therapy of Leaky Gut AndreaMichielanandRenataDIncà.
This last finding has been subject to much. 1Department of Pediatrics McMaster University Hamilton Ontario. What is not in doubt is that intestinal permeability in patients with Crohns disease is increased proportional to disease activity.
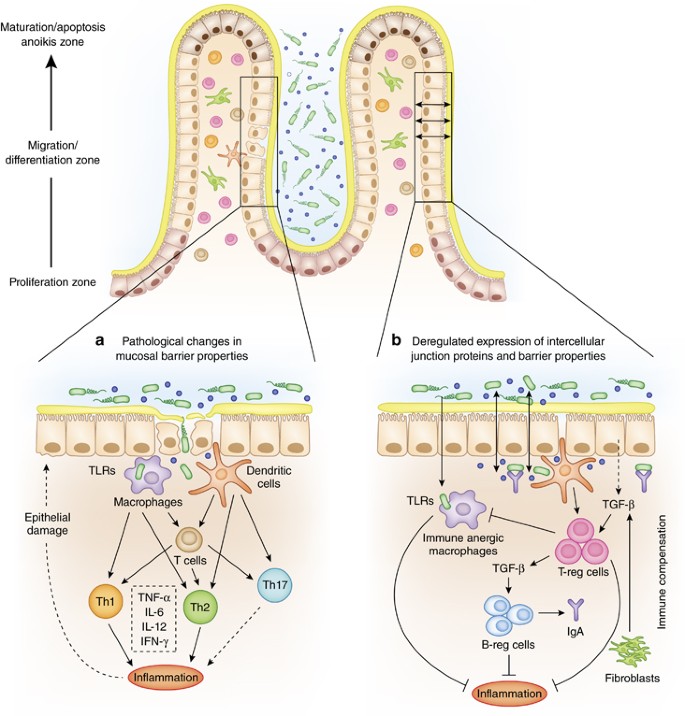
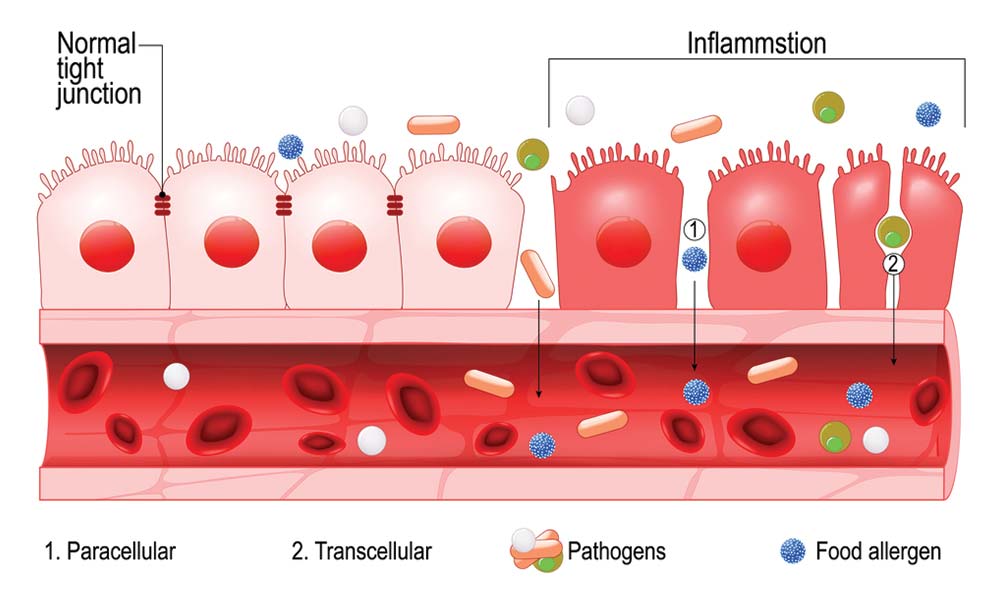
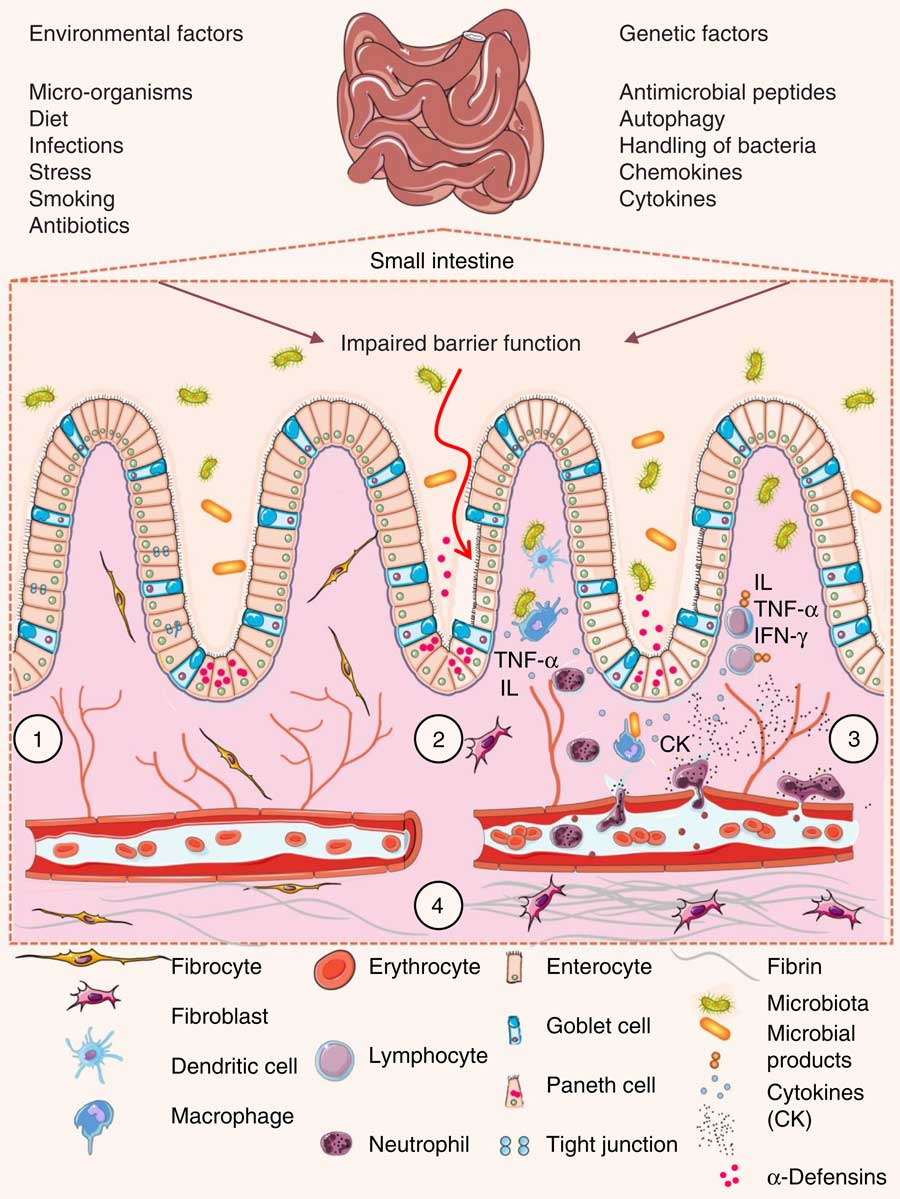
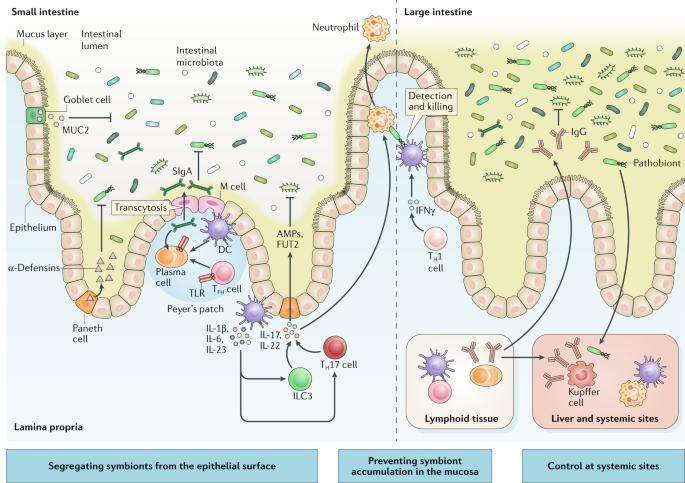
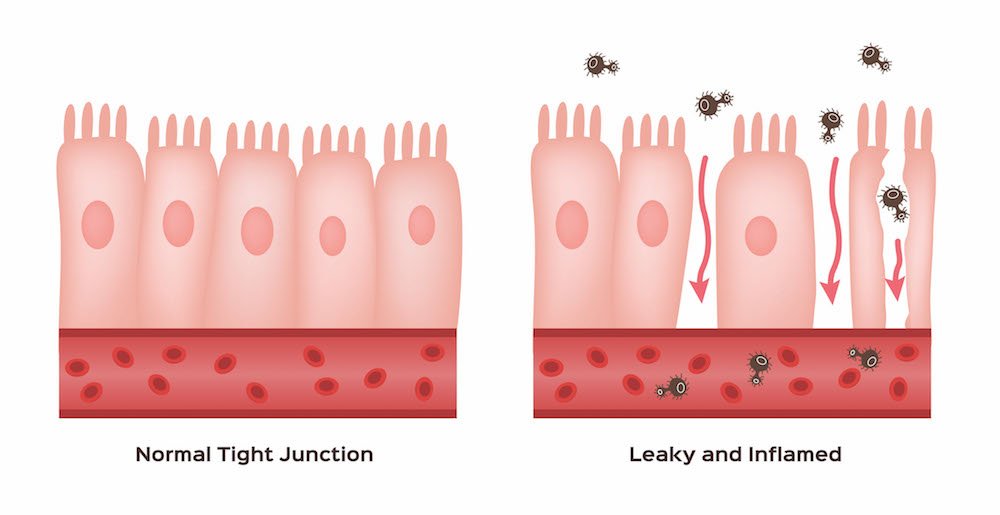
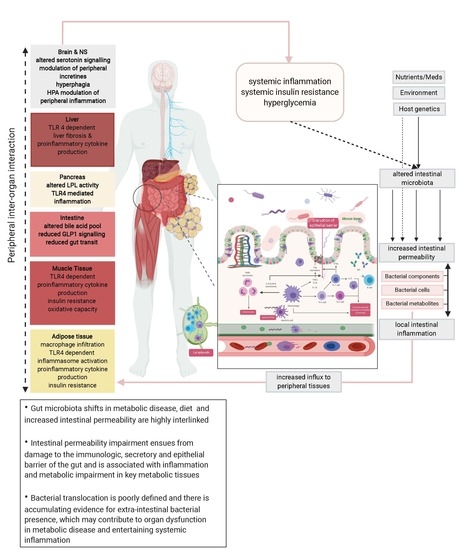
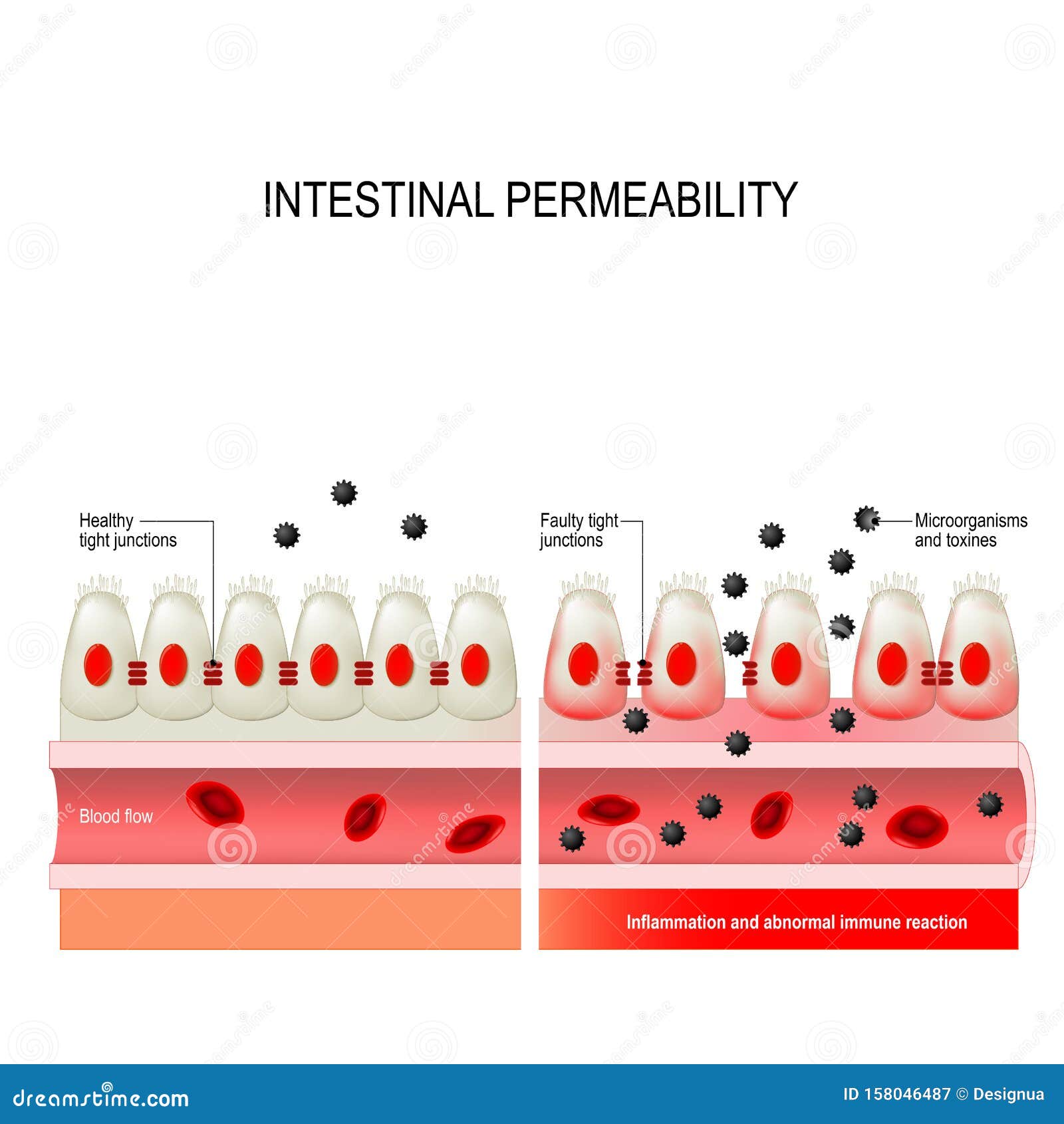
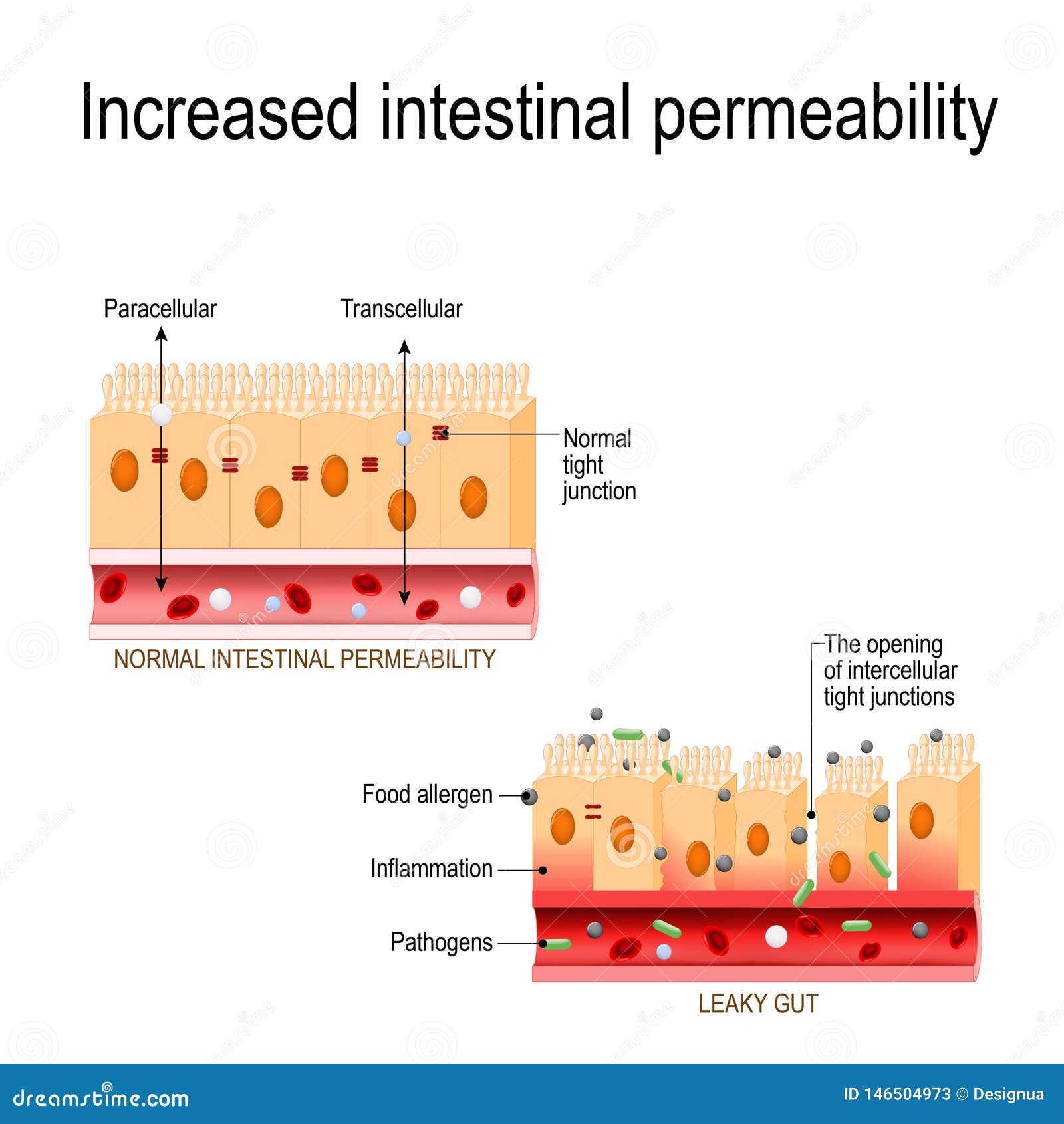
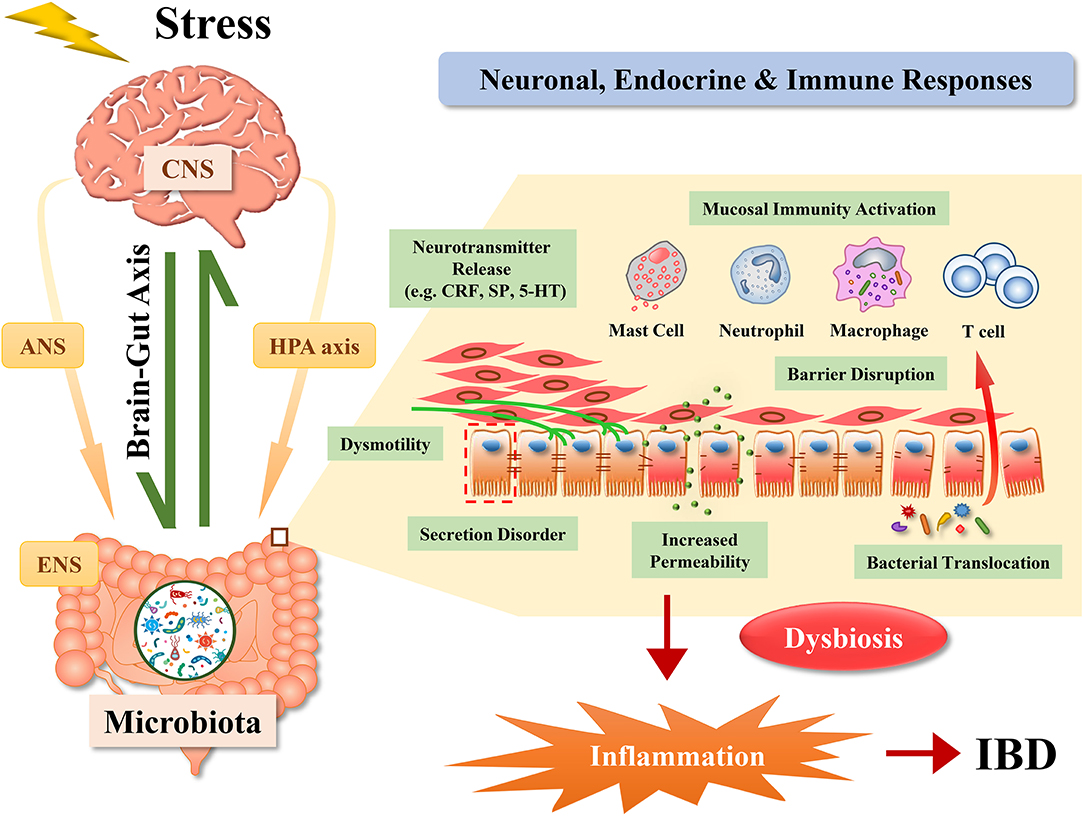
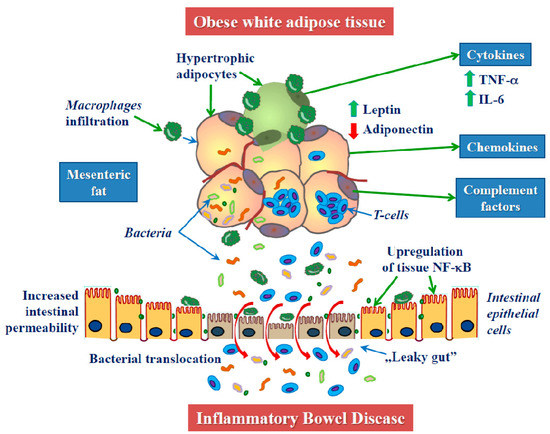
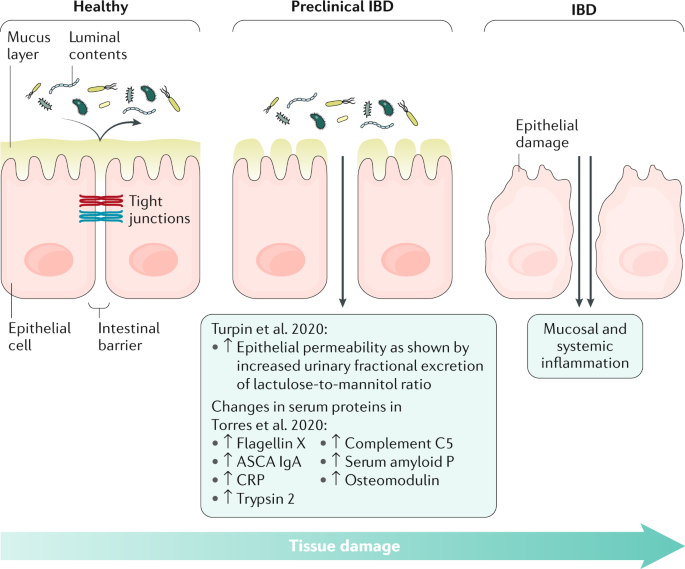
Intestinal permeability compared in pediatric and adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease. The pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease IBD is multifactorial with data suggesting the role of a disturbed interaction between the gut and the intestinal microbiota. A defective mucosal barrier may result in increased intestinal permeability which promotes the exposition to luminal content and triggers an immunological response that promotes intestinal inflammation.
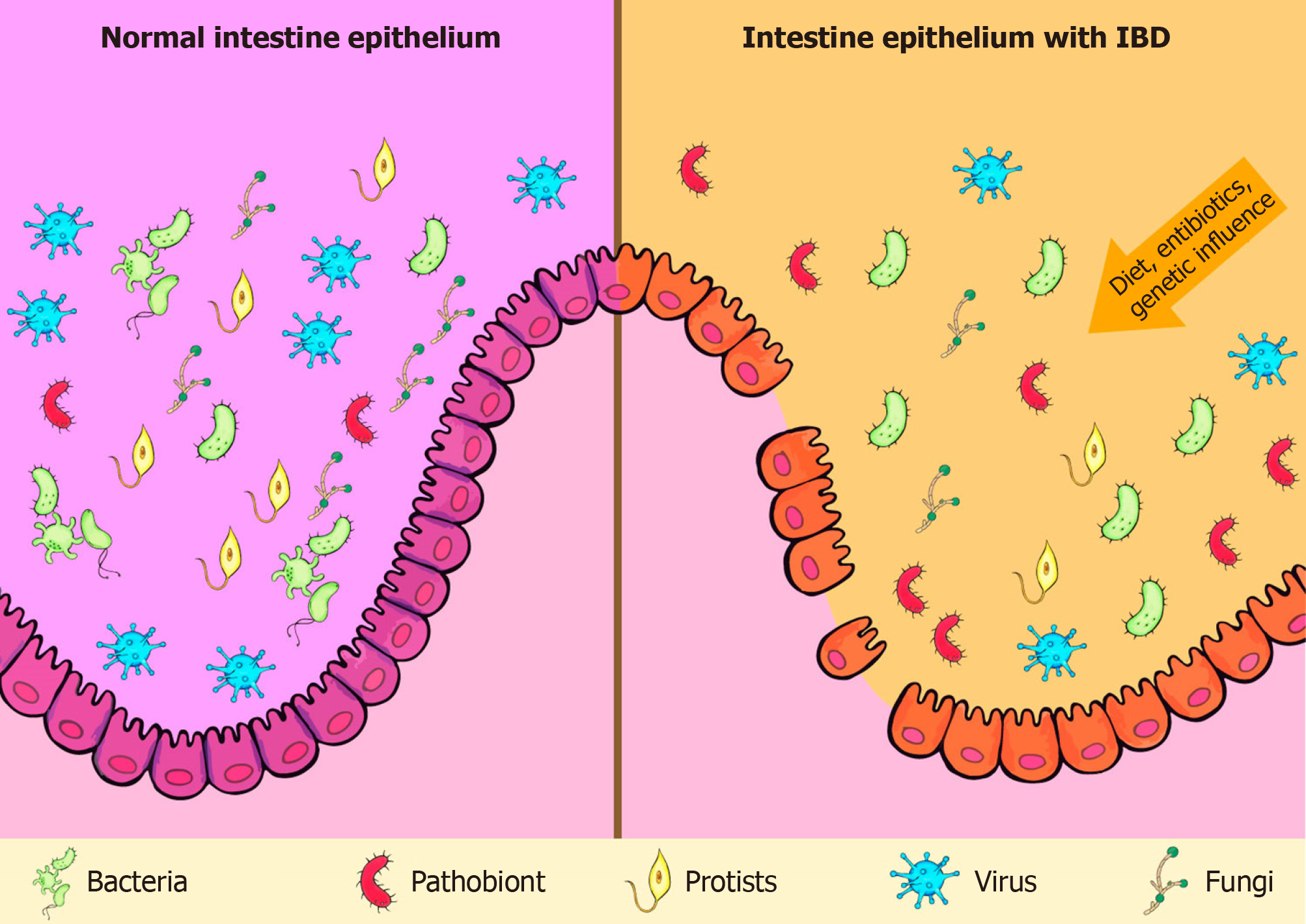
Promotion of pro-inflammatory intestinal microbiota. The normal structure of the gut microbiome and its alterations in IBD were defined in several microbial studies. Dietary components such as omega-6 fatty acids long-chain fatty acids protein and digestible carbohydrates may contribute to IBD pathogenesis through altering intestinal microbiota increasing intestinal permeability and promoting inflammation.
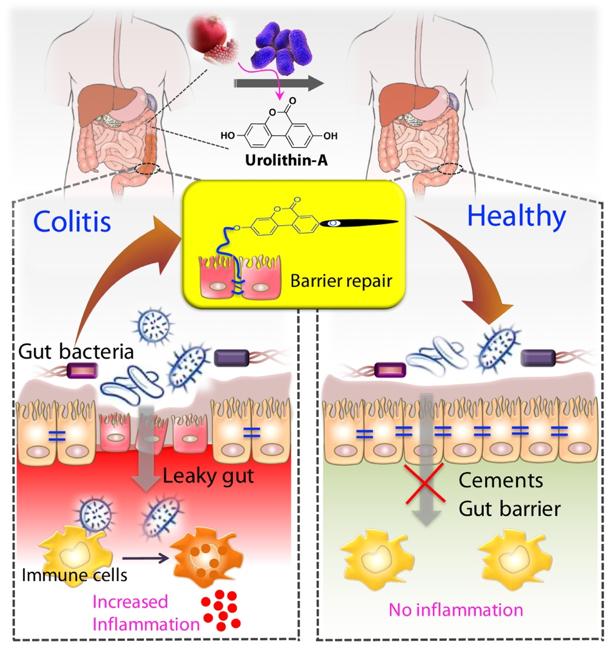
Concentrations of glycoalkaloids normally available while eating potatoes can adversely affect the mammalian intestine and can aggravate IBD. The pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease IBD is multifactorial with data suggesting the role of a disturbed interaction between the gut and the intestinal microbiota. Further to these cell and animal studies have demonstrated plausible mechanisms by which dietary emulsifiers may contribute to IBD pathogenesis through mechanisms including.
Whereas omega-3 fatty acids medium chain triglycerides and nondigestible carbohydrates improve these parameters and intestinal health. Functional tests such as the sugar absorption tests or the novel imaging. Issenman RM1 Jenkins RT Radoja C.
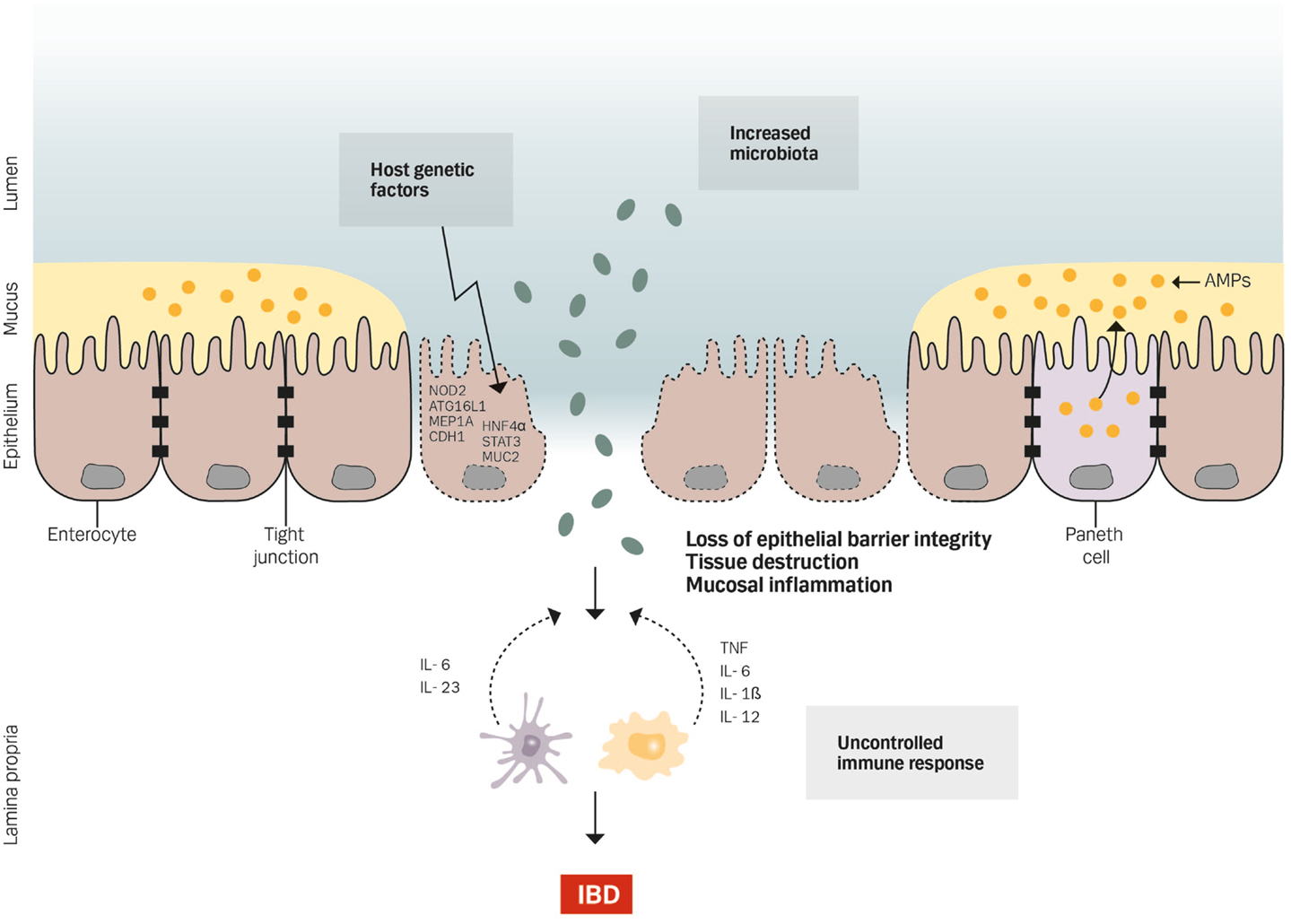
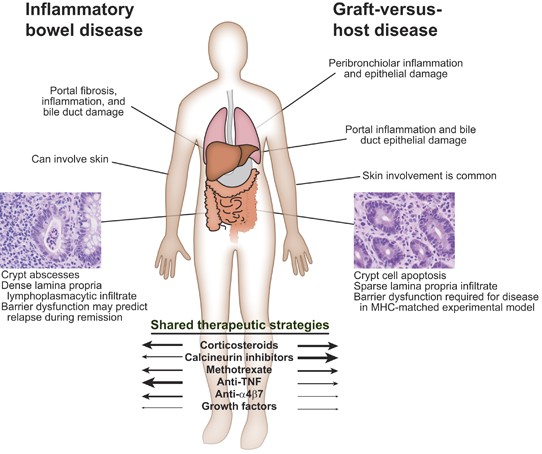
Life and all the metabolic processes depend either directly or indirectly on proper functioning of GI tract. Two different conditions are included in inflammatory bowel disease IBD Crohns disease CD and ulcerative colitis UC being distinguished by chronic recurrence of gut inflammation in persons that are genetically predisposed and subjected to environmental causative factors.
Dietary components such as omega-6 fatty acids long-chain fatty acids protein and digestible carbohydrates may contribute to IBD pathogenesis through altering intestinal microbiota increasing intestinal permeability and promoting inflammation.
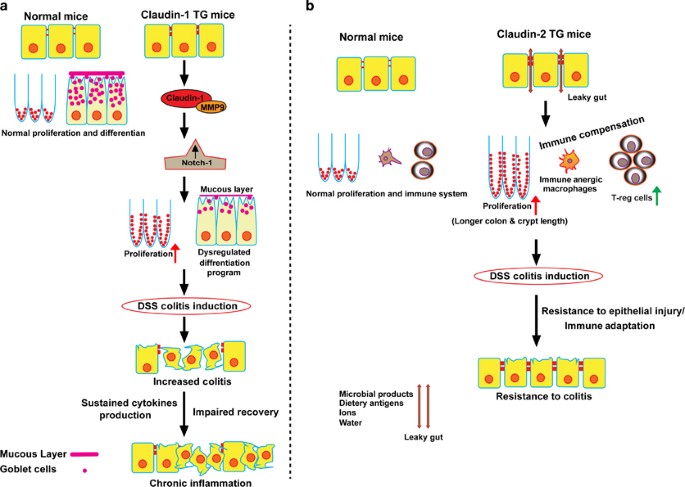
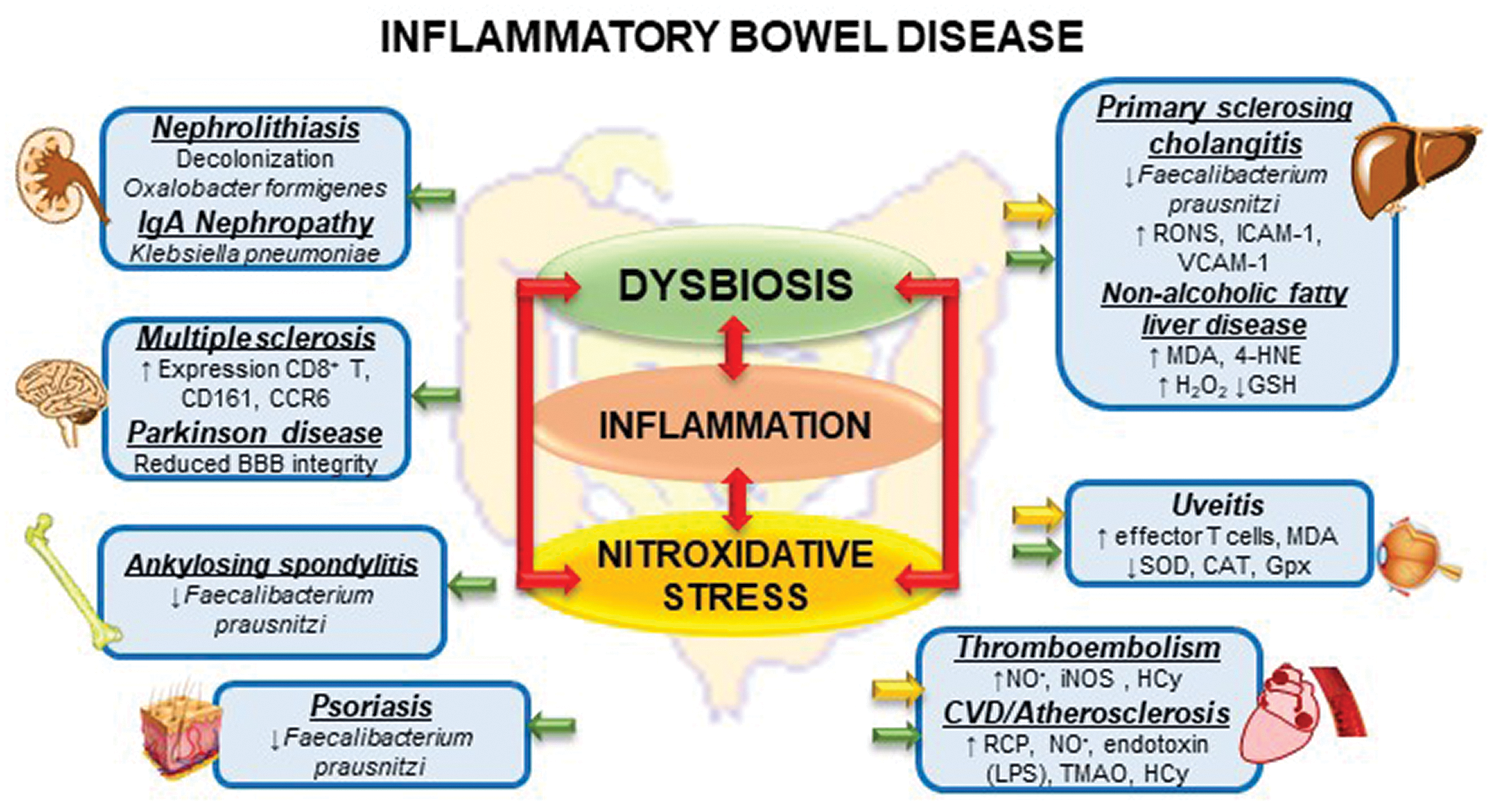
Issenman RM1 Jenkins RT Radoja C. And a small proportion of first-degree relatives have increased intestinal permeability. Two different conditions are included in inflammatory bowel disease IBD Crohns disease CD and ulcerative colitis UC being distinguished by chronic recurrence of gut inflammation in persons that are genetically predisposed and subjected to environmental causative factors. Dietary components such as omega-6 fatty acids long-chain fatty acids protein and digestible carbohydrates may contribute to IBD pathogenesis through altering intestinal microbiota increasing intestinal permeability and promoting inflammation. Inflammatory bowel diseases IBD are characterized by a chronic inflammatory process that affects the intestinal barrier structure. 1Department of Pediatrics McMaster University Hamilton Ontario. Concentrations of glycoalkaloids normally available while eating potatoes can adversely affect the mammalian intestine and can aggravate IBD. The pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease IBD is multifactorial with data suggesting the role of a disturbed interaction between the gut and the intestinal microbiota. In clinical practice several studies have documented that changes in intestinal permeability can predict IBD course.
Potato glycoalkaloids adversely affect intestinal permeability and aggravate inflammatory bowel disease. Life and all the metabolic processes depend either directly or indirectly on proper functioning of GI tract. It can be used to predict clinical relapse of disease and prognosis. Potato glycoalkaloids adversely affect intestinal permeability and aggravate inflammatory bowel disease. The physical chemical and microbial challenges to this barrier are intensified in the intestinal tract due to the presence of food and the symbiotic microbial community. A defective mucosal barrier may result in increased intestinal permeability which promotes the exposition to luminal content and triggers an immunological response that promotes intestinal inflammation. Functional tests such as the sugar absorption tests or the novel imaging.




























Post a Comment for "Intestinal Permeability And Inflammatory Bowel Disease"